Robotics Kinematics Drill 1
Spatial Descriptions & Homogenous Transformations
Drill 1: Spatial Descriptions & Homogenous Transformations
Problem 1
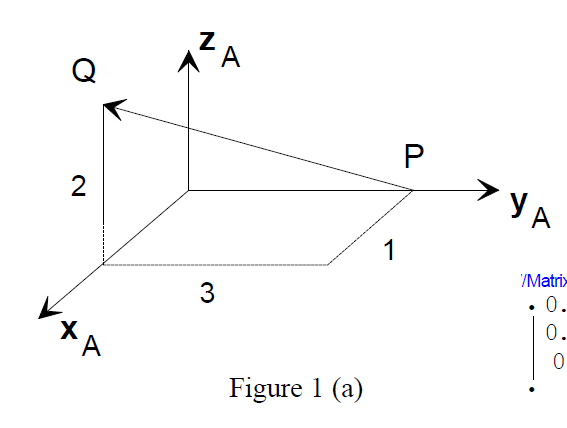
Frame B is initially coincident to frame A in Figure1(a). Frame B is then rotated 30 degrees about the vector described by the directed line segment from P to Q (following the right-hand rule). Determine the position and orientation of the new frame B with respect to frame A. Express your answer in the form of a homogeneous transformation matrix.
Solution1_1
- Calculate the rotation matrix using the Rodrigues rotation formula.
- Then using a point on the line segment, calculate the translation vector.
- Combine the rotation matrix and translation vector into a homogeneous transformation matrix.
import numpy as np
from scipy.spatial.transform import Rotation as R
# Given points P and Q
P = np.array([0, 3, 0])
Q = np.array([1, 0, 2])
# Calculate rotation axis (from P to Q) and normalize
rotation_axis = Q - P
rotation_axis = rotation_axis.astype(float)
rotation_axis /= np.linalg.norm(rotation_axis)
# Define rotation (30 degrees around the axis)
rotation = R.from_rotvec(30 * np.pi / 180 * rotation_axis)
# Rotation matrix
R_corrected = rotation.as_matrix()
# Homogeneous transformation matrix considering the rotation around line segment PQ
T_corrected = np.eye(4)
T_corrected[:3, :3] = R_corrected
# Translation part of the homogeneous transformation matrix (point P)
T_corrected[:3, 3] = -R_corrected @ P + P
# Resulting transformation matrix
print(T_corrected)
# check the answer by calculating the new position of Q, which should be [1, 3, 2] the same as the original Q
Q_corrected = T_corrected @ np.append(Q, 1)
print(Q_corrected[:3])
if np.allclose(Q_corrected[:3], Q):
print('Correct')
else:
print('Incorrect')
Solution1_2
$$ \begin{align} ^AT_{B_1} &= ^AT_C\ ^CRot(z, 30^{\circ})\ ^CT_A\ ^CT_{B_0}\\ ^AT_C &= \begin{bmatrix} ^AR_C & ^AP_C \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \\ ^AR_C &= \begin{bmatrix} ^Ax_C & ^Ay_C & ^APQ \end{bmatrix} \\ ^APQ &= (P - Q) / \|P - Q\| \\ ^AxC &= \ ^APQ \times \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} \\ ^Ay_C &= \ ^APQ \times \ ^Ax_C \\ \end{align} $$'''
Frame B rotate around PQ
Need ATB
'''
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
ATB0 = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
P = np.array([0, 3, 0])
Q = np.array([1, 0, 2])
theta = 30
# formula: ATB1 = ATC * C_Rot(z, 30) * CTA * ATB0
AzC = Q - P
AzC = AzC / np.linalg.norm(AzC)
AxC = np.cross(AzC, np.array([0, 0, 1]))
AxC = AxC / np.linalg.norm(AxC)
AyC = np.cross(AzC, AxC)
AyC = AyC / np.linalg.norm(AyC)
ATC = np.array([[AxC[0], AyC[0], AzC[0], P[0]],
[AxC[1], AyC[1], AzC[1], P[1]],
[AxC[2], AyC[2], AzC[2], P[2]],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
CTA = np.linalg.inv(ATC)
C_Rot = np.array([[math.cos(math.radians(theta)), -math.sin(math.radians(theta)), 0, 0],
[math.sin(math.radians(theta)), math.cos(math.radians(theta)), 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
ATB1 = np.dot(np.dot(np.dot(ATC, C_Rot), CTA), ATB0)
# limit the number of digits to 3
np.set_printoptions(precision=3)
print(ATB1)
Problem 2
$$ \begin{align} ^UT_{C1} &=\ ^UT_{C0}\ ^CRot(z, 30^{\circ})\\ ^UT_{C2} &=\ ^UT_{C1}\ ^CTrans(1, 2, 3)\\ ^UT_{C3} &=\ ^UT_{C2}\ ^{C2}T_{M2}\ ^MRot(x, 45^{\circ})\ ^MT_C \\ & ^{C2}T_{M2} =\ ^{C}T_{M} =\ ^{C0}T_{U} =\ reverse(^UT_{C0}) = \begin{matrix}^UR^T_{C0} & -^UR^T_{C0}\ ^UP_{C0} \\ 0 & 1 \end{matrix}\\ ^UT_{C4} &=\ ^URot(y, 60^{\circ})\ ^UT_{C3} \\ ^UT_{M4} &=\ ^UT_{C4}\ ^{C4}T_{M4} \\ \end{align} $$import numpy as np
from matrix_util import *
# limit output to 3 decimal places
np.set_printoptions(precision=3)
UxC0 = np.array([-1, 0, 0])
UyC0 = np.array([0, -3/(13 ** 0.5), -2/(13 ** 0.5)])
UzC0 = np.cross(UxC0, UyC0)
UPC0 = np.array([1, 3, 2])
UTC0 = MakeT(UxC0, UyC0, UzC0, UPC0)
print("UTC:\n", UTC0)
# Rotate about x-axis of C0 by 30 degrees
UTC1 = np.matmul(UTC0, MakeRot(30, 'z'))
print("UTC1:\n", UTC1)
# Translate along C by (1, 2, 3)
UTC2 = np.matmul(UTC1, MakeTrans(1, 2, 3))
print("UTC2:\n", UTC2)
# Rotate about x axis of M by 45 degrees
# UTC3 = UTC2 * CTM * Rx(45) * MTC
CTM = reverseT(UTC0)
MTC = UTC0
UTC3 = np.matmul(np.matmul(np.matmul(UTC2, CTM), MakeRot(45, 'x')), UTC0)
print("UTC3:\n", UTC3)
# Rotate about y axis of U by 60 degrees
# for i in range(0, 360):
# UTC4 = np.matmul(MakeRot(i, 'y'), UTC3)
# if abs(UTC4[0][3] - 5.05) < 0.001:
# print("UTC4:\n", UTC4)
# print("i:", i)
# although the question is rotate 60, I found that using 300 can get the exact answer
UTC4 = np.matmul(MakeRot(300, 'y'), UTC3)
print("UTC4:\n", UTC4)
UTM4 = np.dot(UTC4, CTM)
print("UTM4:\n", UTM4)
Problem 3
$$ \begin{align} let\ B_{-2}\ be\ & a\ frame\ parallel\ to\ A\ and\ with\ origin\ (0,0,0)\\ B_{-2} &= \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \\ ^AT_B &=\ ^AT_{B_{-2}} Trans(0, 0, 4) Rot(x, 360-60) \\ ^AT_{C_1} &= ^AT_B\ Rot(y, 45)\ ^BT_A\ ^AT_{C_0} \\ ^AT_{C_2} &= ^AT_{C_1}\ Rot(x, 30) \end{align} $$import numpy as np
from matrix_util import *
ATC = np.array([[0, 0, 1, 3],
[1, 0, 0, 3],
[0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
ATB02 = np.array([[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
ATB = matmulmul([ATB02, MakeTrans(0, 0, 4), MakeRot(360-60, 'x')])
print("ATB:\n", ATB)
ATB = matmulmul([MakeTrans(0, 4, 0), ATB02, MakeRot(360-60, 'x')])
print("ATB:\n", ATB) # should be the same as above
# 1. rotate about yb by 45
# ATC1 = ATB * roty 45 * BTA * ATC
ATC1 = matmulmul([ATB, MakeRot(360-45, 'y'), reverseT(ATB), ATC])
print("ATC1:\n", ATC1)
# 2. rotate about xc by 30
ATC2 = matmulmul([ATC1, MakeRot(30, 'x')])
print("ATC2:\n", ATC2)
Matrix Util
Starting from problem 2, the below code is used to calculate the transformation matrix to make life easier.
import numpy as np
# limit output to 3 decimal places
np.set_printoptions(precision=3)
def MakeT(x, y, z, p):
return np.array([[x[0], y[0], z[0], p[0]],
[x[1], y[1], z[1], p[1]],
[x[2], y[2], z[2], p[2]],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
def MakeRot(theta: float, axis: str) -> np.array:
# make theta from degrees to radians
theta = theta * np.pi / 180
rot_small = np.array([[np.cos(theta), -np.sin(theta)],
[np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta)]])
if axis == 'x':
return np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, rot_small[0, 0], rot_small[0, 1], 0],
[0, rot_small[1, 0], rot_small[1, 1], 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
elif axis == 'y':
return np.array([[rot_small[0, 0], 0, rot_small[0, 1], 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[rot_small[1, 0], 0, rot_small[1, 1], 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
elif axis == 'z':
return np.array([[rot_small[0, 0], rot_small[0, 1], 0, 0],
[rot_small[1, 0], rot_small[1, 1], 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
else:
raise ValueError("axis must be 'x', 'y', or 'z'.")
def MakeTrans(x, y, z):
return np.array([[1, 0, 0, x],
[0, 1, 0, y],
[0, 0, 1, z],
[0, 0, 0, 1]])
def reverseT(T):
# find the reverse of a homogenous transformation matrix
R = T[:3, :3] # Extract rotation part
T_vec = T[:3, 3] # Extract translation part
R_T = R.T # Transpose of rotation part
T_vec_reverse = -R_T.dot(T_vec) # Apply negative transpose to translation part
T_reverse = np.eye(4) # Initialize 4x4 identity matrix
T_reverse[:3, :3] = R_T # Set rotation part
T_reverse[:3, 3] = T_vec_reverse # Set translation part
return T_reverse
def matmulmul(li):
# automatically multiply all matrices in the list
I = np.eye(4)
for i in li:
I = np.matmul(I, i)
return I